What Is a Rigid Flex Board?
Rigid Flex Board
A rigid flex board is a hybrid circuit board that combines elements of flexible and rigid circuit boards. It consists of a rigid PCB with flex ribbon segments that connect to each other to provide flexibility and structural integrity. Rigid flex circuit boards are ideal for applications that require the board to bend or conform to specific form factors without compromising electrical performance.
Many common products incorporate rigid flex board, including laptop computers, smartphones, and wearable devices. The bending capabilities of rigid flex are ideal for these types of devices, as they can conform to the user’s hand, for example. In these cases, rigid flex PCBs eliminate the need for connectors and flexible cables that would otherwise need to be routed to each individual component within the device. This can result in a more compact and space-efficient electronic assembly, as well as reduced manufacturing costs.
Rigid flex circuit boards are also a good choice for high-reliability applications, such as aerospace and medical devices. These boards are designed to withstand continuous mechanical stress and can be bent or folded repeatedly without suffering from physical failure. In addition, rigid flex circuit boards can be used in applications where the device may experience environmental conditions such as shocks, vibrations, or temperature variations.
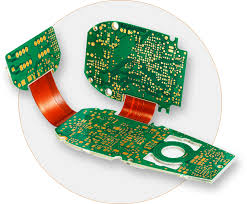
What Is a Rigid Flex Board?
The hybrid construction of rigid flex PCBs makes them more complex to design than traditional rigid PCBs. However, the design process can be made easier with integrated MCAD and ECAD tools that operate in 3D. Having access to these tools in a single application allows you to better visualize your rigid flex PCB and understand how it will bend or conform to its physical environment. This can help reduce the risk of costly errors in manufacturing and assembly, especially if your rigid flex PCB will undergo dynamic or constant flexing.
As you begin to design your rigid flex PCB, it’s important to consider the layout and component placement as well as the underlying structure. Ensure that the rigid and flex sections are properly connected using the correct connections, vias, and traces. You’ll want to take into account a variety of environmental considerations, including moisture resistance, corrosion protection, and thermal cycling. It’s also essential to ensure that the flex section can withstand repeated bending and flexing without failing mechanically.
Once your rigid flex PCB is fully designed, it’s time to prepare the board for manufacturing. This involves generating Gerber files, assembly drawings, and more. You can easily do this with a unified design platform like Altium Designer, which offers standard routing, layout, and CAD tools in 3D, along with the necessary tools for designing rigid-flex PCBs.
Rigid flex PCBs offer a number of benefits, including space efficiency, durability, and versatility. With fewer components and connections, these circuit boards can reduce assembly costs while improving reliability by eliminating the need for connectors that are prone to failure. In addition, they can be bent or twisted to fit into tight spaces, making them a great option for compact and densely packed electronic assemblies.